You can find the configuration of the WWAN Bridge Mode in LANconfig under .
- Mode
-
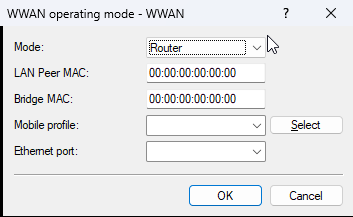
Defines the operating mode of the device’s internal mobile interface. Possible values:
- Router
- In Router Mode, the device establishes the cellular connection itself and obtains an IP address on its WWAN interface. A downstream network gains Internet access via Network Address Translation (NAT).
- Bridge
- In Bridge Mode, the device acts as a transparent network bridge and forwards all IP packets from the mobile network to exactly one downstream device. Detailed bridge configuration is performed in the LAN Bridge settings.
- LAN Peer MAC
- MAC address of the device or client in the LAN that should receive the IP address directly from the mobile network. If the MAC address is 0, the MAC address learned from received packets is used automatically.
- Bridge MAC
- MAC address to be used as the sender address. If the MAC address is 0, a “locally administered” address derived automatically from the device’s MAC address is used.
- Mobile profile
- Defines the WWAN profile to be used.
- Ethernet port
- Defines the Ethernet port, e.g. ETH-1, on which the device signals in WWAN bridge mode by briefly bringing the Ethernet port up and down that the WWAN connection has been interrupted or re-established. In bridge mode, the WWAN router acts solely as a modem and transparently forwards the cellular connection (WWAN) to the downstream router. The downstream router then assumes all routing functionality (NAT, DHCP, firewall, etc.). In this case, the WWAN router is not responsible for address assignment or routing. If the WWAN connection is disconnected or re-established while the router is operating in bridge mode, the following problems may occur: The downstream router may incorrectly assume that the WWAN connection is still active and therefore display incorrect status information and attempt to send data over this connection. For WWAN connections with a dynamic IP address, the router uses the old, no longer valid IP address while in the error state. To avoid these problems, the WWAN bridge router must send an "Ethernet Port Down / Port Up" signal to the Ethernet port that is connected to the downstream router in the event of a connection failure. When the cellular modem changes state (disconnecting and establishing the cellular connection), the WWAN router physically switches off the Ethernet port for a few seconds. This mechanism reliably informs the downstream router that the connection has been interrupted, allowing it to delete the default route, restart the DHCP client or mark the old IP address as no longer valid, and signal the failure of the cellular connection to the user. Ideally, the WWAN bridge device should be connected directly to the downstream router via an Ethernet cable so that the downstream router reliably detects the state change. If this type of installation is not possible, the downstream router should perform IP polling to actively monitor the logical Internet connection.
