You can make global content filter settings in LANconfig under :
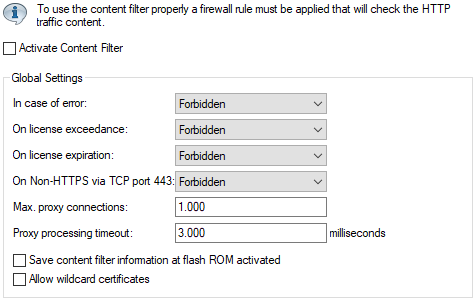
- Activate Content Filter
- This allows you to activate the content filter.
- In case of error
- This lets you define what happens in the event of an error. For example, if the rating server cannot be reached, this setting determines whether the user can browse freely or if all web access is blocked.
- On license expiration
- The license for using LANCOM Security Essentials is valid for a specific period. You will be reminded of the upcoming license expiration 30 days, one week, and one day in advance (to the email address configured in LANconfig under ).
- Here, you can specify whether websites should be blocked or passed through unchecked after license expiration. Based on this setting, the user can either browse freely after the license expires or all web access will be denied.
-
Note: To ensure the reminder is actually sent to the specified email address, you must configure the appropriate SMTP account.
- On Non-HTTPS via TCP port 443
- Forbidden
- Disallows non-HTTPS traffic on port 443.
- Allowed
- Allows non-HTTPS traffic on port 443.
Important: If you allow non-HTTPS connections on port 443, the traffic will not be classified but instead generally permitted. By default, non-HTTPS traffic on port 443 is not allowed.- Max. proxy connections
- Set the maximum number of simultaneous proxy connections allowed. This helps limit system load. A notification is triggered if this number is exceeded. You can configure the type of notification under .
- Proxy processing timeout
- Specify the time in milliseconds the proxy is allowed for processing. If this time is exceeded, a timeout error page is returned.
- Save Content Filter information to flash ROM activated
- If enabled, this option stores content filter information in the device’s Flash ROM.
- Allow wildcard certificates
- For websites using wildcard certificates (with CN entries such as *.mydomain.de), enabling this function
uses the main domain (mydomain.de) for filtering. The filtering process occurs in the following order:
- Check the server name in the "Client Hello" (depending on the browser used)
- Check the CN in the received SSL certificate
- Wildcard entries are ignored
- If the CN is not usable, the "Alternative Name" field is evaluated
- DNS reverse lookup of the corresponding IP address and evaluation of the resulting hostname
- If wildcards are included in the certificate, the main domain is used instead (as described above)
- Check the IP address
